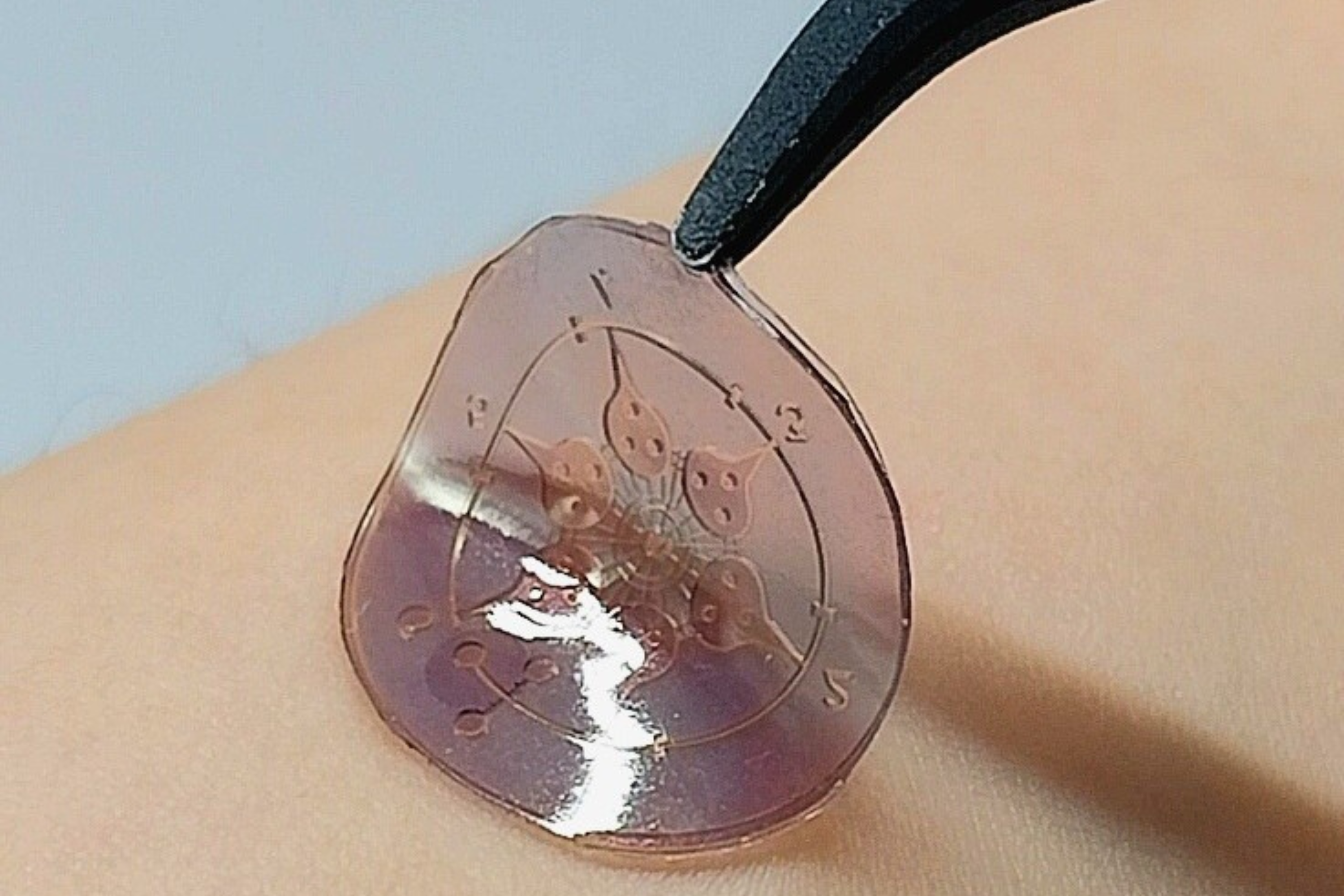
Summary
Researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology have created a wearable patch that can analyze molecules in sweat to monitor health conditions. This patch can detect substances like uric acid and lactate to provide insights into diseases such as gout and liver dysfunction. The technology offers a noninvasive way to track health changes over time compared to traditional blood tests.
Key Facts
- The patch can analyze molecules in sweat, including uric acid, lactate, and tyrosine.
- It can help monitor conditions such as gout, muscle fatigue, and liver dysfunction.
- Unlike blood tests, the patch provides dynamic health information as the body's state changes.
- The patch offers a noninvasive alternative for health tracking during activities.
- It is designed as a low-cost, disposable device that attaches to the skin.
- Researchers plan to expand the patch's capability to detect more molecules, such as glucose, which could help manage diabetes.
- The patch uses a new method that allows it to gather a wide range of molecules without needing special tags or labels.